Klebsiella pneumoniae treatment
Since Klebsiella pneumoniae is a bacterium for treatment using antibiotics.
However, the treatment of infections caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae is always problematic, because the bacterium is naturally resistant to benzylpenicillin (penicillin G) and aminopenicillins (ampicillin) holds. These usually become further acquired resistance.
Therefore a useful antibiotic therapy is only after isolation of the pathogen and the creation of an antibiogram possible, since only an effective antibiotic can be selected.
Some patients with a urinary tract infection treated successfully with antibiotics suffer, soon after recovery, the same infection again. So kill the antibiotics used reliably even really all bacteria? This issue will be resolved in a research project at the University of Wuerzburg.
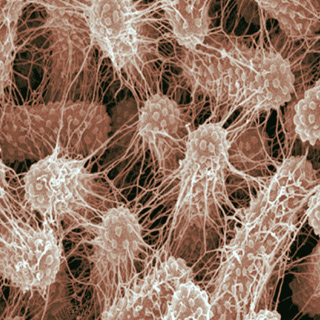
Like little pills from Klebsiella pneumoniae see the bacteria that have attached to a cell of the bladder mucosa. The photograph shows an early stage of urinary tract infection, the bacteria are still outside the cells.
|
Urinary tract infections are infections by the respiratory tract, the second most common form of infectious diseases. The majority of urinary tract infections with antibiotics can cure so far.
If some patients suffer periodically after an initially successful treatment relapses, then it is often the same pathogens responsible, who had already caused the first infection. One reason could be that the pathogen can penetrate into the mucosal cells of the urinary bladder or in certain cells of the kidney.
|
Inside the cells, the bacteria are then relatively well protected from the immune system, but also from the effects of many antibiotics: is used to treat an antibiotic that destroys only the bacteria outside of the mucosal cells, then survive all the bacteria in the cells . stop After stopping the antibiotics, the survivors left their hiding place and again cause an acute urinary tract infection.
Antibiotics are active against the Klebsiella pneumoniae
| Name | Dosage | |
| Moxifloxacin | 400 mgs | once a day intravenously |
| Ofloxacin | 400 - 800 mgs | once a day |
| Levofloxacin | 250 - 750 mgs | once a day |
| Sparfloxacin | 400 mgs at first day, 200 mgs at other days | once a day at morning |
| Ceftriaxone | 1 -2 g once a day | not more than 10 days. The introduction of the drug is recommended to continue for another 2-3 days after normalization of body temperature and symptoms disappear. |
| Betamethasone | once or twice a day | 2 - 4 weeks |
| Ampicillin | 250 - 500 mgs every 6 hours | 0.5 - 1 hour before a meal for 5 - 14 days |
| Prostate extract | 1 supp. | rectal at once a day for 10 -14 days |
| Ceftobiprole | 500 mgs | every 8 hours for 7 - 14 days |
| Ertapenem | 1 g | once a day for 3 - 14 days |
| Cefotaxime | 1 - 2 g | every 8 - 12 hours |
| Cefepime | 500 mgs - 1 g | twice a day for 7 - 10 days |
| Meropenem | 500 mgs - 1 g | every 8 hours |
| Fosfomycin | 3 g at 2 hour before a meal at night | 1 - 2 times |
| Ofloxacin | 400 mgs | twice a day before a meal for 7 - 10 days |
| Terizidone | 900 mgs (1 capsule 3 times a day) | 3 - 4 months |
| Pyobacteriofag | | 1 -3 times a day for 5 - 15 days |
| Cefixime | 400 mgs | once a day for 7 - 10 days |
| Tobramycin | 1 mgs/kg | 1-3 times a day for 5 - 10 days |
| Gemifloxacin | 320 mgs | once a day for 7 days |
| Betamethasone + Gentamycin | | 3-4 times a day for 10 days |
|
|